When you’re out in the wilderness, the ability to build a shelter can be a lifesaving skill. A tarp is a versatile and lightweight material that can be used to build a wide range of shelter structures. Tarpology, the art of tarp shelter building, is an essential skill for anyone who spends time in the great outdoors.
Materials Needed for Tarp Shelter Building
To build a tarp shelter, you’ll need a few materials:
- A tarp
- Paracord or other sturdy cordage
- Tent stakes or other anchoring devices
- A hiking pole (ideal for the tent setup)
Choosing the Right Tarp
There are a variety of tarps available on the market, but for shelter building, you want to look for one that is lightweight, durable, and has a reinforced edge with grommets. You also want to make sure the tarp is large enough to cover the area you want to protect. A 10′ x 12′ tarp is a good size for most shelter building applications. Personally I use a DD Tarp at 3m x 3m as a go to tarp.
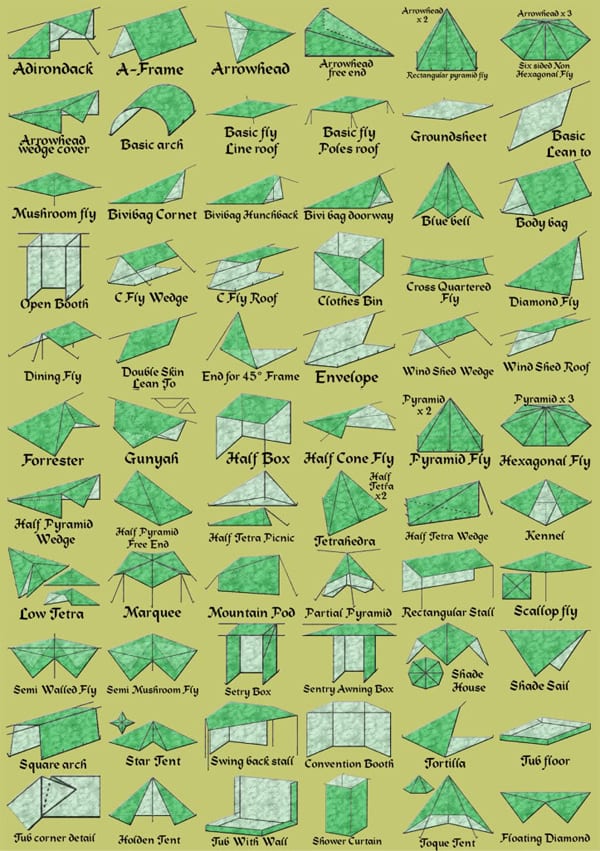
Types of Tarp Shelters
There many different types of tarp shelters you can build as you can see from this blogs picture. Here are four main ones:
- Lean-to Shelter – This is a simple shelter that requires one anchor point, such as a tree or a stake. The tarp is anchored at the top and stretched out to create a sloping roof. The bottom of the tarp is then anchored to the ground with stakes.
- A-Frame Shelter – This shelter is similar to a lean-to, but requires two anchor points. The tarp is anchored at the top of each anchor point and then staked out at the bottom to create a triangular A-frame shape.
- Diamond Shelter – This shelter is created by folding the tarp in half diagonally to form a triangle. The two corners opposite the fold are anchored to trees or stakes, and the other two corners are staked to the ground.
- Tarp Tent – This shelter is created by folding the tarp in half, and then anchoring the two corners opposite the fold to trees or stakes. The other two corners are then staked to the ground, creating a tent-like structure.
Tips for Building a Tarp Shelter
- Choose a location that is protected from the wind and rain.
- Clear the area of any debris or sharp objects that could damage the tarp.
- Use a ground cloth or sleeping pad to insulate yourself from the ground.
- Be sure to properly anchor the tarp to the ground and any anchor points.
- Adjust the tension on the tarp to ensure a tight and secure shelter.
- Always carry extra cordage and stakes in case of emergency or equipment failure.
